Free Microsoft AZ-104 Exam Dumps - Page 14
Hotspot
You have an Azure subscription that contains an Azure Storage account.
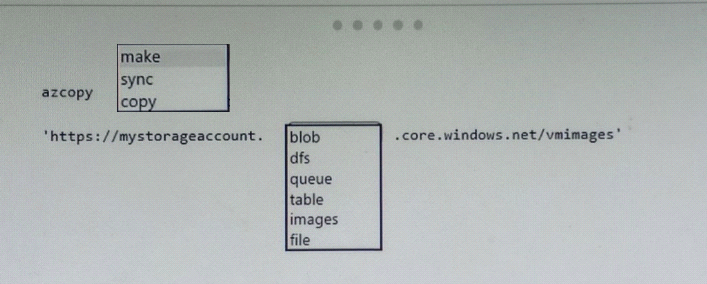
You plan to copy an on-premises virtual machine image to a container named vmimages.
You need to create the container for the planned image.
Which command should you run? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
Explanation
Box 1:make
Here the purpose is to 'create a container". So the correct command would be azcopy make.
Box 2: blob
The requirement is for storing that image, it's not used to build AKS. So blob is correct option.
Hotspot
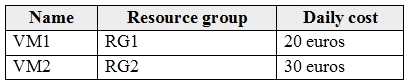
You have a pay-as-you-go Azure subscription that contains the virtual machines shown in the following table.
You create the budget shown in the following exhibit.
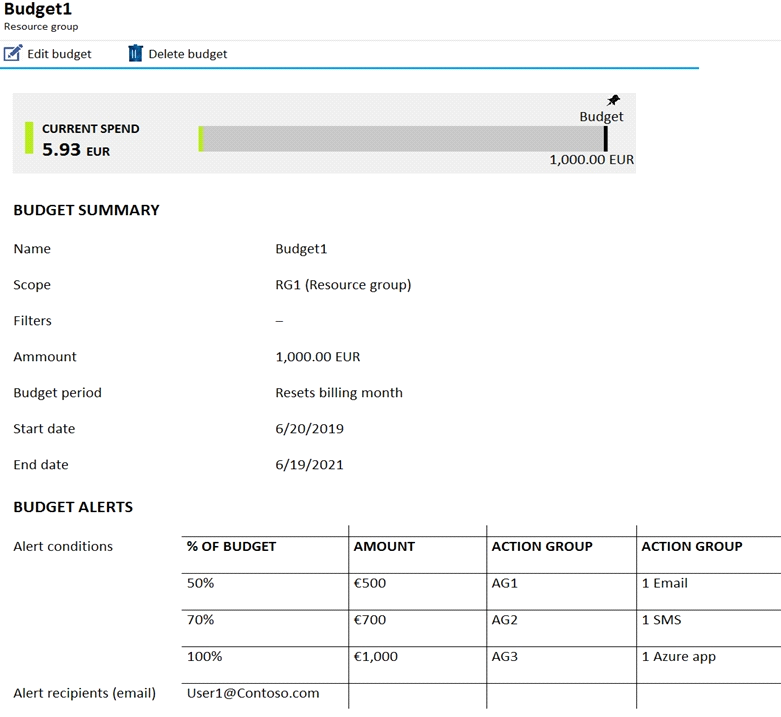
The AG1 action group contains a user named admin@contoso.com only.
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Box 1: VM1 and VM2 continues to run
When the budget thresholds you've created are exceeded, only notifications are triggered. None of your resources are affected and your consumption isn't stopped. You can use budgets to compare and track spending as you analyze costs.
Box 2: one email notification will be sent each month
Budget alerts for Resource Group RG1, which include VM1, but not VM2.VM1 consumes 20 Euro/day. The 50% ,500 Euro limit, will be reached in 25 days, and an email will be sent.
The 70% and 100% alert conditions will not be reached within a month, and they don't trigger email actions anyway.
References:
Hotspot
You have an Azure subscription named Subcription1 that contains a resource group named RG1.
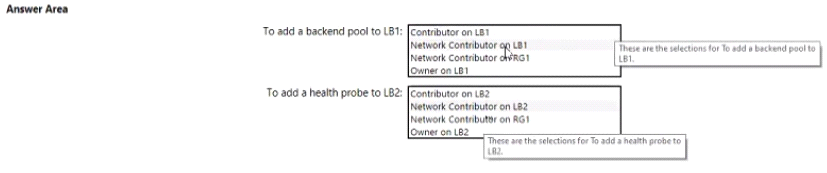
In RG1. you create an internal load balancer named LB1 and a public load balancer named 162.
You need to ensure that an administrator named Admin 1 can manage LB1 and LB2. The solution must follow the principle of least privilege.
Which role should you assign to Admin1 for each task? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Caen correct selection is worth one point.
Explanation
Box 1: Network Contributor on RG1
To add to the backend pool, write permission is required on the Resource Group because it writes deployment information. To add a backend pool, you need network contributor role on the LB and on the VMs that will be part of the backend pool.
For this reason the network contributor role must be assigned to the RG where the LB and the VM resides. So the correct answer is Network Contributor on RG1 .
Box 2: Network Contributor on RG1
For Health Probe also, without having access to RG1, no health probe can be added. If only Network Contributor role is assigned to LB then the user would not be able to access the IP addresses of the member pools.
Owner/Contributor can give the user access for everything. So it will not fit into the the principle of least privilege. Hence Owner and contributor role is incorrect choices for the question.
Hotspot
You have an Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) tenant named contoso.com that contains the users shown in the following table:
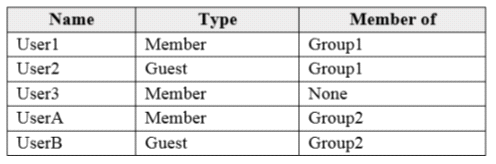
User3 is the owner of Group1.
Group2 is a member of Group1.
You configure an access review named Review1 as shown in the following exhibit:
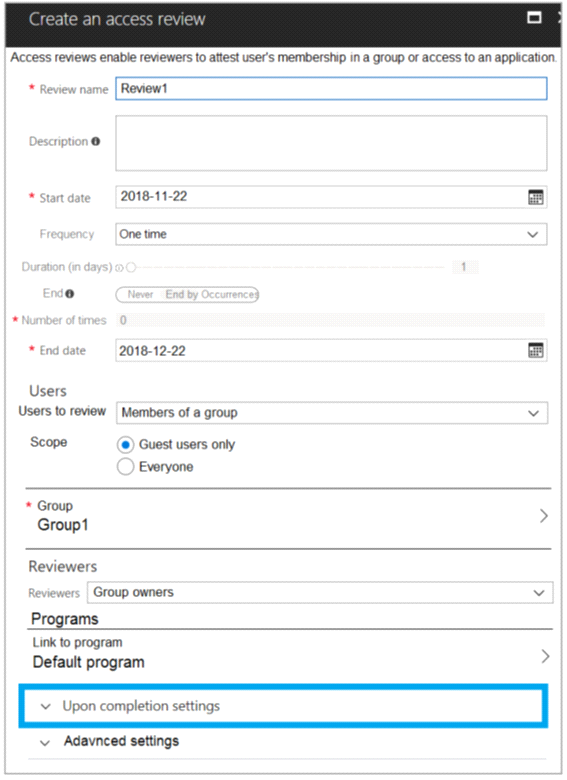
For each of the following statements, select Yes if the statement is true. Otherwise, select No.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Explanation
In theUserssection, specify the users that the access review applies to. Access reviews can be for the members of a group or for users who were assigned to an application. You can further scope the access review to review only the guest users who are members (or assigned to the application), rather than reviewing all the users who are members or who have access to the application.

Present Use Case:
Group2 is a member of Group1 and User3 is the owner of Group1 So User3 can review both Group 1 and 2.
But for review the scope says only Guest.
Solution:
User1 is a member not a guest so 1st statement ==> NO
UserA is member not the guest so 2nd statement ==> No
UserB is a guest so 3rd statement ==> Yes
Hotspot
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscription1 contains two Azure virtual machines named VM1 and VM2. VM1 and VM2 run Windows Server 2016.
VM1 is backed up daily by Azure Backup without using the Azure Backup agent.
VM1 is affected by ransomware that encrypts data.
You need to restore the latest backup of VM1.
To which location can you restore the backup? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
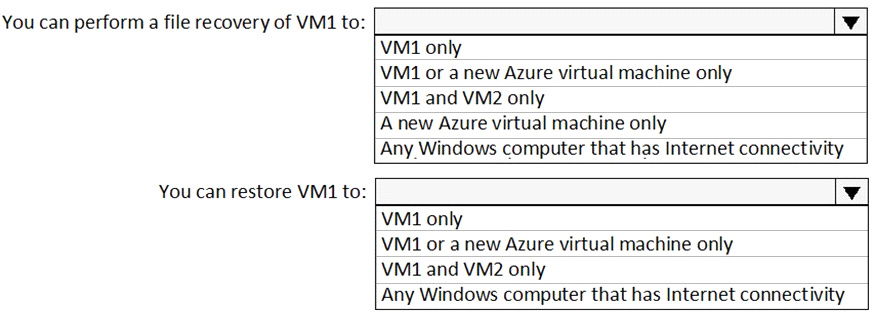
Box 1 : VM1 and VM2 only
When recovering files, you can't restore files to a previous or future operating system version.You can restore files from a VM to the same server operating system, or to the compatible client operating system. Therefore -
"VM1 and VM2 only" is the best answer since both run on Windows Server 2016.
"A new Azure virtual machine only" ,this will also work but why to create unnecessary new VM in Azure if existing VM will do the task. So this option is incorrect.
Box 2 : VM1 or A new Azure virtual machine only
References:
Hotspot
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1.
In Subscription1, you create an Azure file share named share1.
You create a shared access signature (SAS) named SAS1 as shown in the following exhibit.
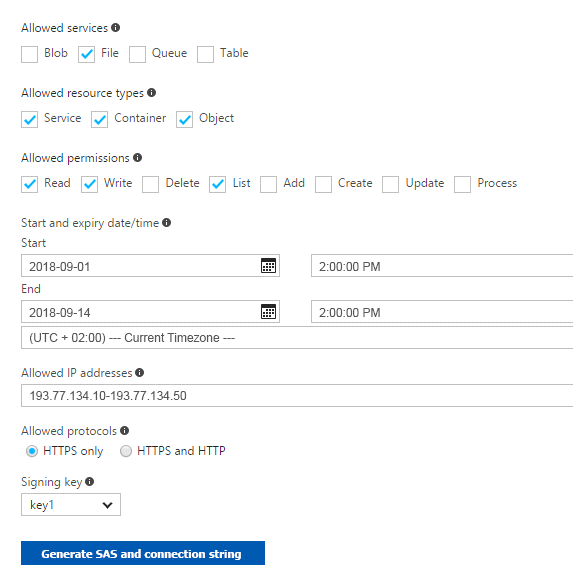
To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Explanation
Box 1: will have no access
The IP 193.77.134.1 does not have access on the SAS since this IP falls outside of the allowed IP address range for SAS. Hence "will have no access" is correct.
Box 2: will be prompted for credentials
The net use command is used to connect to file shares.To mount an Azure file share, you will need the primary (or secondary) storage key. SAS keys are not currently supported for mounting. Based on the provided SAS exhibit, IP address is an allowed IP and also on given date SAS is active, but account storage key is must to have to run the "net use" command , which is not provided in the question. Hence "will be prompted for credentials" is correct option for this.
net use R: \rebelsa1.file.core.windows.net\rebelshare
References:
MultipleChoice
Question: 153
Note: This question is part of a series of questions that present the same scenario. Each question in the series contains a unique solution that might meet the stated goals. Some question sets might have more than one correct solution, while others might not have a correct solution.
After you answer a question in this section, you will NOT be able to return to it. As a result, these questions will not appear in the review screen.
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscription1 contains a resource group named RG1. RG1 contains resources that were deployed by using templates.
You need to view the date and time when the resources were created in RG1.
Solution: From the RG1 blade, you click Automation script.
Does this meet the goal?
OptionsHotspot
You have an Azure subscription named Subscription1. Subscription1 contains a virtual machine named VM1.
You install and configure a web server and a DNS server on VM1.
VM1 has the effective network security rules shown in the following exhibit.
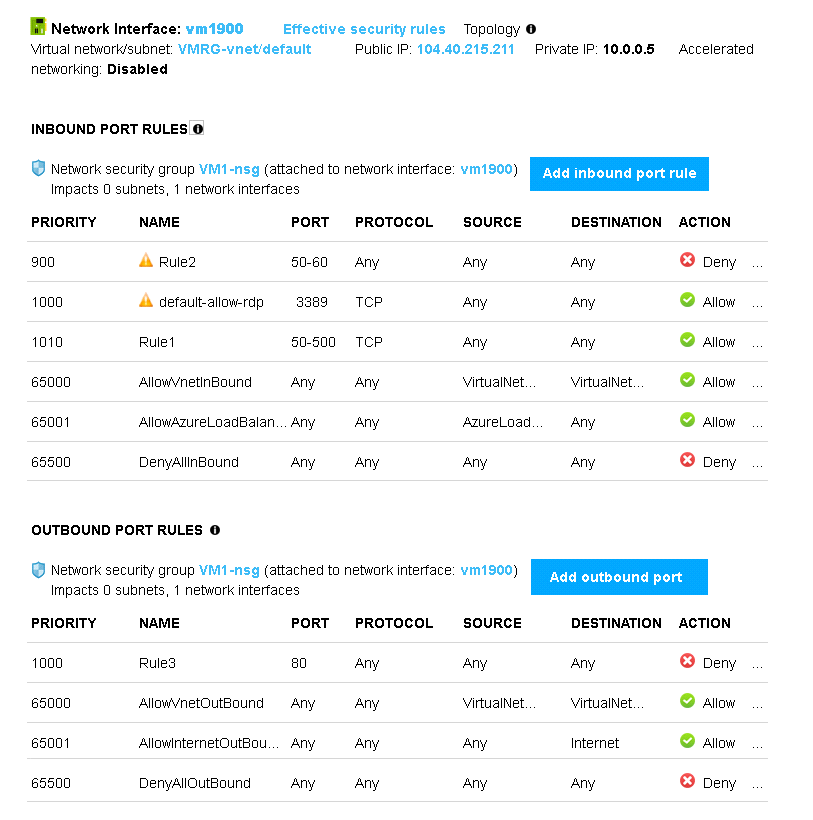
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.

Box 1:
Rule2 blocks ports 50-60, which includes port 53, the DNS port. Internet users can reach the Web server, since it uses port 80.
Box 2:
If Rule2 is removed internet users can reach the DNS server as well.
Note:Rules are processed in priority order, with lower numbers processed before higher numbers, because lower numbers have higher priority. Once traffic matches a rule, processing stops. As a result, any rules that exist with lower priorities (higher numbers) that have the same attributes as rules with higher priorities are not processed.
References:
Hotspot
You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtual machine scale set. The scale set contains four instances that have the following configurations:
Operating system: Windows Server 2016
Size: Standard_D1_v2
You run the get-azvmss cmdlet as shown in the following exhibit:
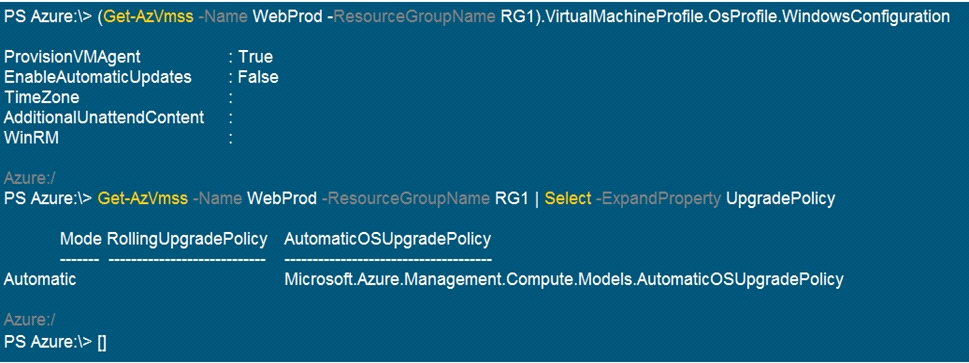
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement based on the information presented in the graphic.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
he Get-AzVmssVM cmdlet gets the model view and instance view of a Virtual Machine Scale Set (VMSS) virtual machine.
Box 1: 0
The enableAutomaticUpdates parameter is set to false. To update existing VMs, you must do a manual upgrade of each existing VM.
Box 2: 1
Below is clearly mentioned in the official Website
"The upgrade orchestrator identifies the batch of VM instances to upgrade, with any one batch having a maximum of 20% of the total instance count, subject to a minimum batch size of one virtual machine."
So, 20% from 4 ~1
Hotspot
You have an Azure subscription that contains a virtual network named VNet1. VNet1 uses an IP address space of 10.0.0.0/16 and contains the subnets in the following table.
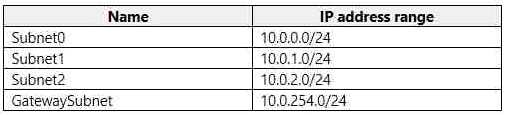
Subnet1 contains a virtual appliance named VM1 that operates as a router.
You create a routing table named RT1.
You need to route all inbound traffic to VNet1 through VM1.
How should you configure RT1? To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.
NOTE: Each correct selection is worth one point.
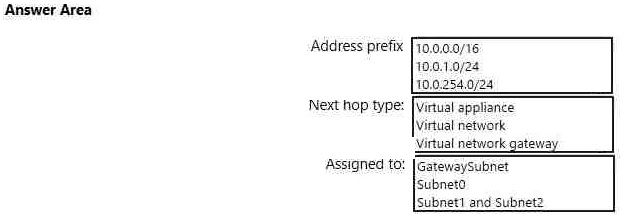
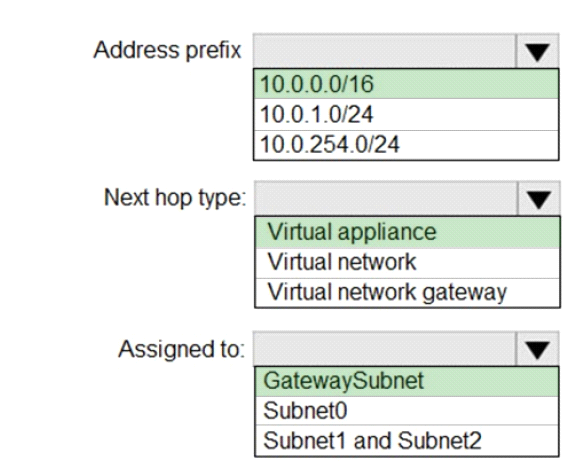
Box1 : 10.0.0.0/16
Address prefix in networking refer to the destination IP address range. In this scenario, destination is Vnet1 , hence Address prefix will be the address space of Vnet1.
Box 2 : Virtual appliance
Next hop gets the next hop type and IP address of a packet from a specific VM and NIC. Knowing the next hop helps you determine if traffic is being directed to the intended destination, or whether the traffic is being sent nowhere
Next Hop --> VM1 --> Virtual Appliance (You can specify IP address of VM 1 when configuring next hop as virtual appliance)
Box 3 : GatewaySubnet
In the scenario it is asked for all the inbound traffic to Vnet1. Inbound traffic is flowing through SubnetGW. You need to route all inbound traffic from the VPN gateway to VNet1 through VM1.So its traffic from Gateway subnet only.

