CFA Institute Exam CFA-Level-II Topic 3 Question 9 Discussion
Topic #: 3
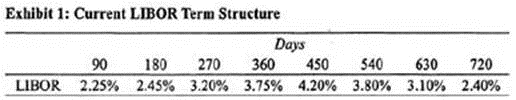
William Bow, CFA, is a risk manager for GlobeCorp, an international conglomerate with operations in the technology, consumer products, and medical devices industries. Exactly one year ago, GlobeCorp, under Bow's advice, entered into a 3-year payer interest rate swap with semiannual floating rate payments based on the London interbank offered rate (LIBOR) and semiannual fixed rate payments based on an annual rate of 2.75%. At the time of initiation, the swap had a value of zero and the notional principal was set equal to $150 million. The counterparty to GlobeCorp's swap is NVS Bank, a commercial bank that also serves as a swap dealer. Exhibit 1 below summarizes the current LIBOR term structure.
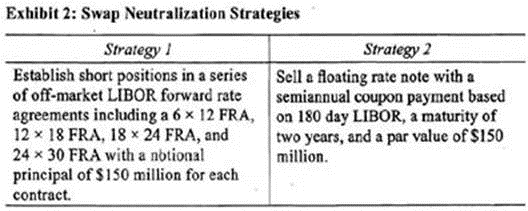
Upper management at GlobeCorp feels that the original swap has served its intended purpose but that circumstances have changed and it is now time to offset the firm's exposure to the swap. Because they cannot find a counterparty to an offsetting swap transaction, management has asked Bow to come up with alternative measures to offset the swap exposure. Bow created a report for the management team which outlines several strategies to neutralize the swap exposure. Two of his strategies are included in Exhibit 2.
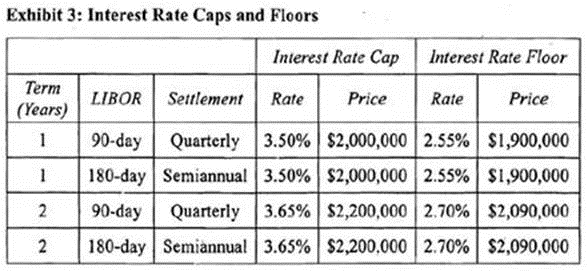
After examining its long-term liabilities, NVS Bank has decided that it currently needs to borrow $100 million over the next two years to finance its operations. For this type of funding need, NVS generally issues quarterly coupon short-term floating rate notes based on 90-day LIBOR. NVS is concerned, however, that interest rates may shift upward and the LIBOR curve may become upward sloping. To manage this risk, NVS is considering utilizing interest rate derivatives. Managers at the bank have collected quotes on over-the-counter interest rate caps and floors from a well known securities dealer. The quotes, which are based on a notional principal of $100 million, are provided in Exhibit 3.
One of the managers at NVS Bank, Lois Green, has expressed her distrust of the securities dealer quoting prices on the caps and floors. In a memo to the CFO, Green suggested that NVS use an alternative but equivalent approach to manage the interest rate risk associated with its two-year funding plan. Following is an excerpt from Green's memo:
"Rather than using a cap or floor, NVS Bank can effectively manage its exposure to interest rates resulting from the 2-year funding requirement by taking long positions in a series of put options on fixed-income instruments with expiration dates that coincide with the payment dates on the floating rate note."
"As a cheaper alternative, NVS can effectively manage its exposure to interest rates resulting from the 2-ycar funding requirement by creating a collar using long positions in a series of call options on interest rates and long positions in a series of call options on fixed income instruments all of which would have expiration dates that coincide with the payment dates on the floating rate note."
Which of the following combinations of interest rate derivatives from Exhibit 3 would effectively limit the maximum and minimum interest cost associated with NVS Bank's $100 million floating rate notes?
An interest rate collar consists of a long interest rate cap and a short interest rate floor. The long cap limits the interest rate exposure on the upside, effectively capping the maximum interest rate the purchaser of the cap will have to pay. The short floor creates exposure to interest rates on the downside, requiring payments as interest rates fall. Because NVS Bank is short a floating rate note, its interest costs should fall with interest rates. However, the short floor limits the degree to which interest expense can fall, effectively limiting the minimum interest payment. The combination of the maximum interest rate and the minimum interest rate creates the collar within which the interest rate may fluctuate. NVS Bank is exposed to quarterly floating rate interest payments for a period of two years. To create an appropriate collar, the bank should purchase the 2-year quarterly settlement cap and sell the 2-year quarterly settlement floor. (Study Session 17, LOS 62.a)
Currently there are no comments in this discussion, be the first to comment!