CFA Institute Exam CFA-Level-II Topic 3 Question 71 Discussion
Topic #: 3
Bryan Stephenson is an equity analyst and is developing a research report on Iberia Corporation at the request of his supervisor. Iberia is a conglomerate entity with significant corporate holdings in various industries. Specifically, Stephenson is interested in the effects of Iberia's investments on its financial performance and has decided to focus on two investments: Midland Incorporated and Odessa Company.
Midland Incorporated
On December 31, 2007, Iberia purchased 5 million common shares of Midland Incorporated for 80 million. Midland has a total of 12.5 million common shares outstanding. The market value of Iberia's investment in Midland was 89 million at the end of 2008 and 85 million at the end of 2009. For the year ended 2008, Midland reported net income of 30 million and paid dividends of 10 million. For the year ended 2009, Midland reported a loss of 5 million and paid dividends of 4 million.
During 2010, Midland sold goods to Iberia and reported 20% gross profit from the sale. Iberia sold all of the goods to a third party in 2010.
Odessa Company
On January 2, 2009, Iberia purchased 1 million common shares of Odessa Company as a long-term investment. The purchase price was 20 per share and on December 31, 2009, the market price of Odessa was 17 per share. The decline in value was considered temporary. For the year ended 2009, Odessa reported net income of 750 million and paid a dividend of 3 per share. Iberia considers its investment in Odessa as an investment in financial assets.
In addition, Iberia has a number of foreign investments, so Stephenson's supervisor has asked him to draft a report on accounting methods and ratio analysis. The following are statements from Stephenson's research report.
Statement 1: Under U .S . GAAP, firms are required to use proportionate consolidation to account for joint ventures.
Statement 2: In general, if the parent's consolidated net income is positive, the equity method reports a higher net profit margin than the acquisition method.
What amount should Iberia recognize in its 2009 income statement as a result of its investments in Midland and Odessa?
First, calculate the continuously compounded risk-free rate as ln( 1.040811) = 4% and then calculate the theoretically correct futures price as follows:
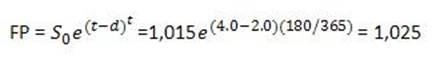
Then, compare the theoretical price to the observed market price: 1.035 - 1,025 = 10. The futures contract is overpriced. To take advantage of the arbitrage opportunity, the investor should sell the (overpriced) futures contract and buy the underlying asset (the equity index) using borrowed funds. Norris has suggested the opposite. (Study Session 16, LOS 59.f)
Tegan
2 months agoNoah
2 months agoAmmie
1 months agoVannessa
1 months agoIesha
2 months agoDetra
2 months agoCarol
2 months agoRana
1 months agoLuis
1 months agoSunny
1 months agoSheron
3 months agoFrancine
2 months agoMargot
2 months agoUna
2 months agoBrynn
3 months agoMadonna
3 months agoNobuko
3 months agoGarry
3 months agoEura
3 months agoGearldine
3 months agoBoris
2 months agoMaynard
2 months agoRyan
3 months agoVicki
3 months agoDorothy
4 months ago